

Maintaining proper water chemistry also helps protect the pool's structure and equipment from corrosion or scaling. Look for projects that are similar in size, complexity, and style to what you envision for your own pool. Freeform or kidney-shaped pools blend naturally with landscaped areas and offer a more organic appearance. Best pool installer nashville TN.
By integrating these water-saving elements, you can enjoy a functional and beautiful pool while using significantly less water." Best nashville pool builders TN. Installing a pool lift or ramp can also help accommodate those with limited mobility.
Tanning ledges and in-pool loungers provide a spa-like feel, while LED lighting sets the mood for nighttime relaxation. For example, unexpected soil conditions may require additional excavation or stabilization work.
Monitor water levels regularly-unexpected drops could indicate a leak that needs immediate attention.
In some instances, a professional inspection or second opinion may help resolve the dispute."
"The perfect pool design enhances your property's aesthetics and suits your family's needs. "Selecting the best construction method for your pool involves weighing several factors, such as budget, desired maintenance level, and design flexibility.


Additionally, a good contractor will take the time to understand your vision, answer your questions, and provide a detailed estimate and timeline. Reputable contractors often provide workmanship warranties alongside manufacturer guarantees on equipment and materials. High-efficiency pumps, heaters, and LED lighting use less energy, resulting in lower utility bills.
In colder climates, winterizing your pool-draining certain components, adding winterizing chemicals, and securely covering the pool-will protect it from freezing conditions. Though they require careful planning and regular maintenance of the natural filtration zones, the environmental and health benefits make them an attractive choice for eco-conscious homeowners."
By choosing recycled options, homeowners demonstrate their commitment to sustainability while creating a stylish and durable pool." Additionally, consider water-saving features like automatic covers and advanced filtration systems that minimize waste.
"Energy-efficient pools often come with higher upfront costs due to advanced equipment, such as variable-speed pumps or solar heaters, but they offer substantial savings in the long run. Routine inspections of heaters, chlorinators, and automation systems help catch potential issues early.
Many manufacturers and contractors require registration to activate the warranty, ensuring that you're covered from the start. Contractors must also be familiar with chemical storage guidelines, filtration system requirements, and water quality testing protocols. "Residential and commercial pools differ significantly in size, usage patterns, and regulatory requirements.
Although fiberglass pools have fewer customization options than concrete, their durability and cost-effectiveness make them a smart investment for many homeowners looking for a long-lasting, easy-to-maintain pool."


Though the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings on utility bills and the reduction in carbon emissions make solar energy a practical and sustainable choice for pool owners." Vinyl-lined pools are budget-friendly and comfortable, though their liners may need replacement over time. Solar covers not only retain heat but also minimize evaporation, saving water and reducing the overall environmental impact.
Having a clear understanding of your warranty terms and maintaining proper records ensures a smooth and efficient resolution." By keeping the water warmer for longer periods, pool covers reduce the need for continuous heating and lower energy consumption.
Using a variable-speed pump allows you to run the system at lower speeds for longer periods, significantly cutting energy usage. It's also important to match the pool's style to your home's architecture, ensuring a cohesive appearance.
"Pool financing options include home equity loans, personal loans, and specialized pool financing programs. Covers also minimize evaporation, which conserves water and keeps chemical levels more stable.
If references highlight recurring issues or poor service, it's a red flag that may prompt you to consider other options." "Selecting the right poolside furniture and decor can elevate the style and comfort of your outdoor area.


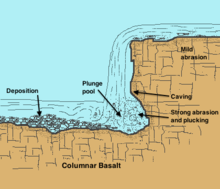
A plunge pool (or plunge basin or waterfall lake) is a deep depression in a stream bed at the base of a waterfall or shut-in. It is created by the erosional forces of cascading water on the rocks at the formation's base where the water impacts.[1] The term may refer to the water occupying the depression, or the depression itself.[2]
Plunge pools are formed by the natural force of falling water, such as at a waterfall or cascade; they also result from man-made structures such as some spillway designs.[3] Plunge pools are often very deep, generally related to the height of the fall, the volume of water, the resistance of the rock below the pool and other factors.[4] The impacting and swirling water, sometimes carrying rocks within it, abrades the riverbed into a basin, which often features rough and irregular sides. Plunge pools can remain long after the waterfall has ceased flow or the stream has been diverted. Several examples of former plunge pools exist at Dry Falls in the Channeled Scablands of eastern Washington.[5] They can also be found underwater in areas that were formerly above sea level, for example, Perth Canyon off the coast of Western Australia.
Plunge pools are fluvial features of erosion which occur in the youthful stage of river development, characterized by steeper gradients and faster water flows. Where softer or fractured rock has been eroded back to a knickpoint, water continues to bombard its base. Because this rock is often less resistant than overlying strata, the water from the higher elevation continues eroding downward until an equilibrium is achieved.
A somewhat similar bowl-shaped feature developed by flowing water, as opposed to falling water, is known as a scour hole. These occur both naturally and as a result of bridge building.
Pool suction-drain injury, also known as suction entrapment, occurs when the drain of a wading pool, swimming pool, hot tub, or fountain sucks in a swimmer's jewelry, torso, limbs, hair or buttocks. In some cases of buttocks entrapment, victims are disemboweled. In the United States, 147 incidents were documented between 1985 and 2002 of which 36 were fatal.[1] In 1982, the Consumer Product Safety Commission reported that five children were disemboweled by drains in wading pools and urged pools to install covers on drains.[2][3]
A standard 8 inches (20 cm) main drain can develop up to 350 pounds (160 kg) of force, which could hold a person underwater in tight grip until the suction is released. This can drown the entrapped person, despite the rescue efforts of multiple adults.[4]
One way to make drains safer is to install shut-off valves and dome-shape drains that are less likely to create a suction effect with the human body, as required in the United States by the 2007 Virginia Graeme Baker Pool and Spa Safety Act. And as a result of that cases nowadays are extremely rare to nonexistent.[5]
| Name | Date | Incident |
|---|---|---|
| Carol Parker | 1957 | A 13-year-old in Prattville, Alabama was sucked feet-first to her hips into a drain of a municipal pool and remained stuck under nine feet of water despite two lifeguards' efforts. She was able to escape the drain when a pool bystander turned off the pump.[6] |
| Valerie Lakey | 1993 | In Cary, North Carolina, 5-year-old Valerie Lakey was disemboweled by a kiddie pool when her bottom became stuck to the drain. Neither turning off the pump nor the strength of four adults dislodged her. The drain cover manufacturer, Sta-Rite, claimed the cover was improperly installed. Lakey survived without most of her small and large intestine and received a $30.9 million settlement from Sta-Rite ($25 million), Wake County, Medfield Area Recreation Club, and others ($5.9 million combined). It was the largest personal injury verdict in North Carolina history and a landmark case of lawyer John Edwards, later a Senator and vice presidential nominee.[7] |
| Virginia Graeme Baker | June 2002 | The seven-year-old granddaughter of former US Secretary of State James Baker died of suction entrapment due to a faulty drain cover and died in her mother's arms at the bottom of a hot tub.[8] The United States Congress passed a pool safety act under her name in 2007.[5] |
| Abigail Taylor | 2007 | The six-year-old died in 2008 nine months after her injury despite subsequent surgeries. Scott and Katey Taylor, her parents, lobbied for the Virginia Graeme Baker Pool and Spa Safety Act, which was passed the year of Abigail's injury.[9] |
| Salma Bashir | 2008 | During a holiday with her family, she was disemboweled while in the kids' swimming pool. As of the time of the report, she was fed by a TPN bag and was waiting for a multiple organ transplant.[10] After getting a small intestine transplant, her body rejected the organ and six months later it was removed, as was her large intestine and gall bladder. She died on January 1, 2024.[11] |
| Evan Pappas | 2018 | Survived an entrapment of 7 minutes 40 seconds in a lazy river in South Carolina in 2018.[12] |
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2010)
|
Salt water chlorination is a process that uses dissolved salt (1000–4000 ppm or 1–4 g/L) for the chlorination of swimming pools and hot tubs. The chlorine generator (also known as salt cell, salt generator, salt chlorinator, or SWG) uses electrolysis in the presence of dissolved salt to produce chlorine gas or its dissolved forms, hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite, which are already commonly used as sanitizing agents in pools. Hydrogen is produced as byproduct too.
The presence of chlorine in traditional swimming pools can be described as a combination of free available chlorine (FAC) and combined available chlorine (CAC).[1] While FAC is composed of the free chlorine that is available for disinfecting the water, the CAC includes chloramines, which are formed by the reaction of FAC with amines (introduced into the pool by human perspiration, saliva, mucus, urine, and other biologics, and by insects and other pests).[2] Chloramines are responsible for the "chlorine smell" of pools, as well as skin and eye irritation. These problems are the result of insufficient levels of free available chlorine, and indicate a pool that must be "shocked" by the addition of 5–10 times the normal amount of chlorine.[1] In saltwater pools, the generator uses electrolysis to continuously produce free chlorine. As such, a saltwater pool or hot tub is not actually chlorine-free; it simply utilizes added salt and a chlorine generator instead of direct addition of chlorine. It also burns off chloramines in the same manner as traditional shock (oxidizer). As with traditionally chlorinated pools, saltwater pools must be monitored in order to maintain proper water chemistry. Low chlorine levels can be caused by insufficient salt, incorrect (low) chlorine-generation setting on the SWG unit, higher-than-normal chlorine demand, low stabilizer, sun exposure, insufficient pump speed, or mechanical issues with the chlorine generator. Salt count can be lowered due to splash-out, backwashing, and dilution via rainwater.

Research has shown that because saltwater pools still use chlorine sanitization, they generate the same disinfection byproducts (DBPs) that are present in traditional pools. Of highest concern are haloketones and trihalomethanes (THMs) of those the predominant form being bromoform. Very high levels of bromoform—up to 1.3 mg per liter, or 13 times the World Health Organization's guideline values—have been found in some public saltwater swimming pools.[3]
Manufacturers have been producing saltwater chlorine generators in the United States since the early 1980s, and they first appeared commercially in New Zealand in the early 1970s (the Aquatech IG4500).[4]
The chlorinator cell consists of parallel titanium plates coated with ruthenium and sometimes iridium. Older models make use of perforated (or mesh) plates rather than solid plates. Electrolysis naturally attracts calcium and other minerals to the plates. Thus, depending on water chemistry and magnitude of use, the cell will require periodic cleaning in a mild acid solution (1 part HCl to 15 parts water) which will remove the buildup of calcium compound crystals, such as calcium carbonate or calcium nitrate. Excessive buildup can reduce the effectiveness of the cell. Running the chlorinator for long periods with insufficient salt in the pool can strip the coating off the cell which then requires an expensive[clarification needed] replacement, as can using too strong an acid wash.
Saltwater pools can also require stabilizer (cyanuric acid) to help stop the sun's UV rays from breaking down free chlorine in the pool. Usual levels are 20–50 ppm. They also require the pH to be kept between 7.2 and 7.8 with the chlorine being more effective if the pH is kept closer to 7.2. The average salt levels are usually in the 3000-5000 ppm range, much less than the ocean, which has salt levels of around 35,000 ppm.[5] In swimming pools, salt is typically poured across the bottom and swept with the pool brush until it dissolves; if concentrated brine is allowed into the return-water system it can cause the chlorinator cell to malfunction due to overconductivity.
Salt water chlorination produces an excess of hydroxide ions, and this requires the frequent addition of hydrochloric acid (HCl, also known as muriatic acid) to maintain pH.[6]
The benefits of salt systems in pools are the convenience and the constant delivery of pure chlorine-based sanitizer. The reduction of irritating chloramines versus traditional chlorinating methods and the "softening" effect of electrolysis reducing dissolved alkali minerals in the water are also perceived as benefits. For some people that have sensitivities to chlorine, these systems may be less offensive.
Disadvantages are the initial cost of the system, maintenance, and the cost of replacement cells. Salt is corrosive and will damage some metals and some improperly-sealed stone. However, as the ideal saline concentration of a salt-chlorinated pool is very low (<3,500ppm, the threshold for human perception of salt by taste; seawater is about ten times this concentration), damage usually occurs due to improperly-maintained pool chemistry or improper maintenance of the electrolytic cell. Pool equipment manufacturers typically will not warrant stainless steel products damaged by saline pools. Calcium and other alkali precipitate buildup will occur naturally on the cathode plate, and sometimes in the pool itself as "scaling". Regular maintenance of the cell is necessary; failure to do so will reduce the effectiveness of the cell. Certain designs of saline chlorinators use a "reverse-polarity" method that will regularly switch the roles of the two electrodes between anode and cathode, causing this calcium buildup to dissolve off the accumulating electrode. Such systems reduce but do not eliminate the need to clean the electrolytic cell and the occurrence of calcium scale in the water.
As chlorine is generated, pH will rise causing the chlorine to be less effective. Many systems with chemistry automation can sense the rising pH and automatically introduce either CO2 or hydrochloric acid in order to bring the pH back to the target level.Automation systems will also manage levels of sanitizer by monitoring the ORP or redox levels of the water. This allows only the needed amount of chlorine to be generated based on the demand.
Sodium bromide can be used instead of sodium chloride, which produces a bromine pool. The benefits and downsides are the same as those of a salt system. It is not necessary to use a chloride-based acid to balance the pH. Also, bromine is only effective as a sanitizer, not as an oxidizer, leaving a need for adding a "shock" such as hydrogen peroxide or any chlorine-based shock to burn off inorganic waste and free up combined bromines. This extra step is not needed in a sodium chloride system, as chlorine is effective as both a sanitizer and an oxidizer. A user would only need to "super chlorinate" or increase chlorine production of the cell occasionally. That would normally be less than once a week or after heavy bather loads.
They do an outstanding job installing beautiful pools and transforming backyards. Winston is exceptional, his communication is top-notch, and he ensures every detail is perfect. Highly recommend!
Winston Farzan has done excellent work for me several times. He's been able to tackle many different jobs at once. I save jobs for him knowing that I can depend on his expertise!
Awesome. I watched a small backyard turn into a backyard oasis. The other options for a smaller pool were either fiberglass or refurbished containers. This is an actual concrete pool with automation. Looks great and I love it!
Above-ground pools are a budget-friendly option that�s quick to install and easy to maintain. They offer flexibility in placement and can be removed or relocated if needed. With proper care, above-ground pools provide years of backyard fun.
Look for a licensed and insured contractor with strong local reviews and a proven track record. Ask about their experience, request a portfolio of completed projects, and compare quotes to find the best fit for your needs.
Fiberglass pools typically last 25�30 years or more with proper maintenance. The durable shell and smooth surface require minimal upkeep compared to other pool types, making fiberglass a long-lasting investment.
Nashville pool builders typically handle the entire pool construction process, including design, excavation, installation, and finishing touches like decking and landscaping. They also offer maintenance and repair services.
Check their licensing, insurance, and experience with local regulations. Reading customer reviews and asking for references can help you find trustworthy installers who deliver quality work on time and within budget.